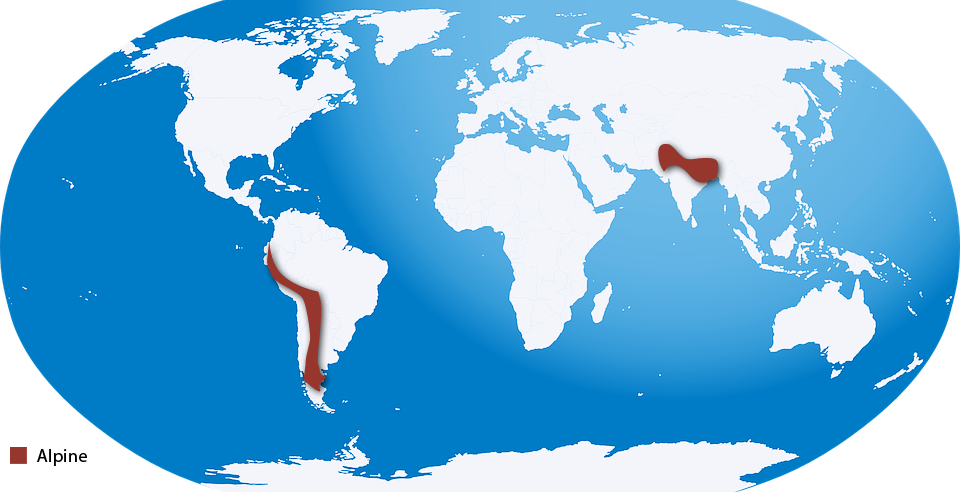
Alpine ecosystems are found in the mountain areas across the globe. One would find them just below the snow line of a mountain. One comes across many ecosystems, as one goes up a mountain, and finally reaches the alpines. For example in India, at high altitudes, generally more than 3600 metres above sea level, temperate forests and grasslands give way to alpine vegetation. The Alpine and Arctic ecosystems, cover 16% of the earth's surface area.
During summers, the average temperatures range from 10 to 15° C . During winters the temperatures drop to freezing point. The winter season lasts from October to May. The summer season lasts from June to September.
Only smaller plants grow here such as tussock grasses, small-leafed shrubs, and dwarf trees. Animals common to this ecosystem are are mountain goats, sheep, elk, beetles, grasshoppers and butterflies.
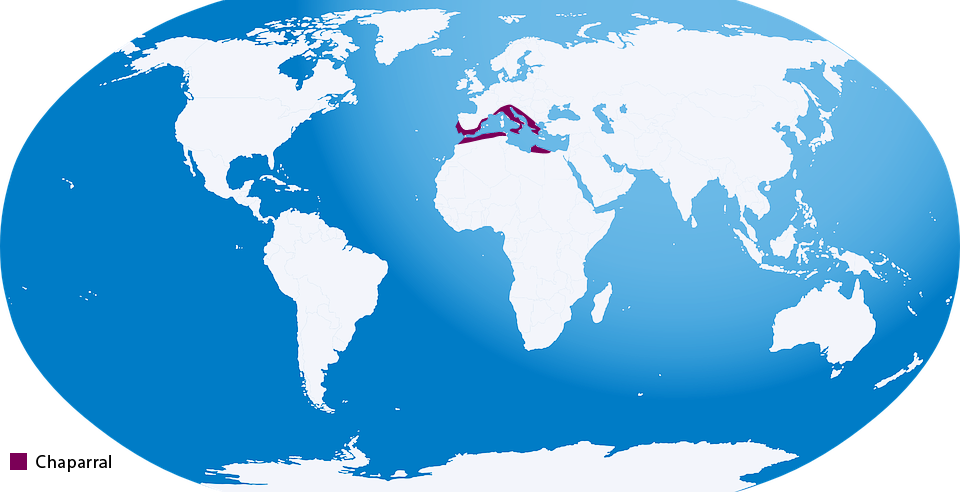
One would find Chaparrals in every continent and it includes mountains and plains. They share similar features with the desert ecosystem. Just like deserts they are hot and dry, but they receive more rainfall per year than the desert ecosystem. The soil found here are poor in nutrients, which makes it vulnerable to erosion.
Chaparrals are very hot and dry. The summers are hot and dry, and temperature reach up to 37.5°C. This makes fires and droughts very common in this ecosystem. The winters are very mild, with temperature about 10°C. It receives most of the rain during winters.
Highly flammable plants are common in this ecosystem, due to which it experiences frequent wildfires. The plants here contain flammable material but their barks can resist fire. Some of the plants found here are poison oak, scrub oak, Yucca Wiple and cacti. Animals common in Chaparral are coyotes, jack rabbits, mule deer, alligator, lizards, horned toads, and praying mantis.
Deciduous forests grow in areas that experience four clear seasons such as winter, spring, summer, and autumn. Deciduous are also called the leaf-shedding forest. As the seasons change in this ecosystem, so do the colours of the leaves. The leaves of some plants fall off during autumn and grow back in the spring. Most temperate, deciduous forests are located in the United States, Canada, Europe, China, and Japan. Some parts of Russia also fall under this ecosystem. The soil in these forests is very fertile.

Deciduous forests receive high rainfall, have warm summers, cooler winters and lose their leaves in winter. These forests receive 30 to 60 inches of rain per annum, which is second only to the rainforests. Summer months usually begin in early June and end in late August. Winter months begin in December.
Broadleaf trees such as oaks, maples, beeches, shrubs, perennial herbs, and mosses are found in deciduous forests. Few examples of animals and birds found in the deciduous forest include the Bald Eagle, Whitetail Deer, Black Bear, Mountain Lion, and Coyote.
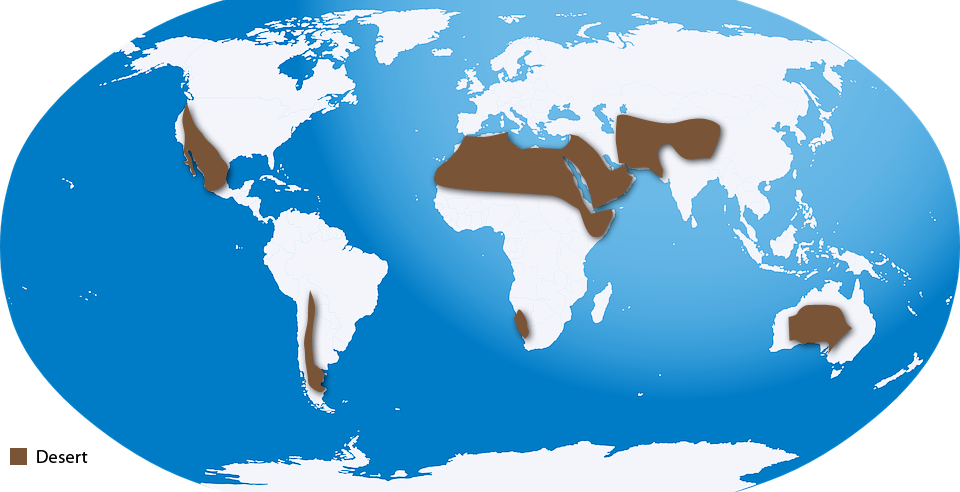
Deserts around the globe can be classified into hot and dry, semiarid, coastal, and cold. Near the Tropic of Cancer or the Tropic of Capricorn, one would find most of the hot and dry deserts. Near the Arctic circle, we find the cold deserts. Each of the deserts have one common feature, which is low level of rainfall each year. Antarctica is the largest cold desert in the world, while the Sahara in Africa is the largest of the hot deserts. The soil in hot deserts is rocky and shallow. The soil in semi-arid deserts can range from soil to rocky. The soil in coastal deserts is smooth and can run through your hands. Cold deserts receive lots of snow.
Weather is not the same in all the desert ecosystems. Average temperature in hot deserts ranges from 18-25°C. Average temperature in semi-arid areas is 26-43°C. In the coastal desert, the summer temperature ranges from 12-22°C.
Plants in hot-deserts adapt to survive in such a dry environment. They are good at storing and finding water. Apart from cacti, barrel cactus, palm trees, desert willow and desert lily are common in this region. Coastal deserts house a variety of plants. These plants also have very thick leaves that can absorb and store water, whenever it is available. Salt bush, rice grass, black sage and chrysothamnus are few examples of plants found in coastal deserts include. In cold deserts, plants such as algae, grasses, and plants with spiny thin leaves. Usually these plants grow only during summer. Lizard, eagles, Great Bustard, Black Buck, wild cats, and fox are commonly found in this ecosystem.
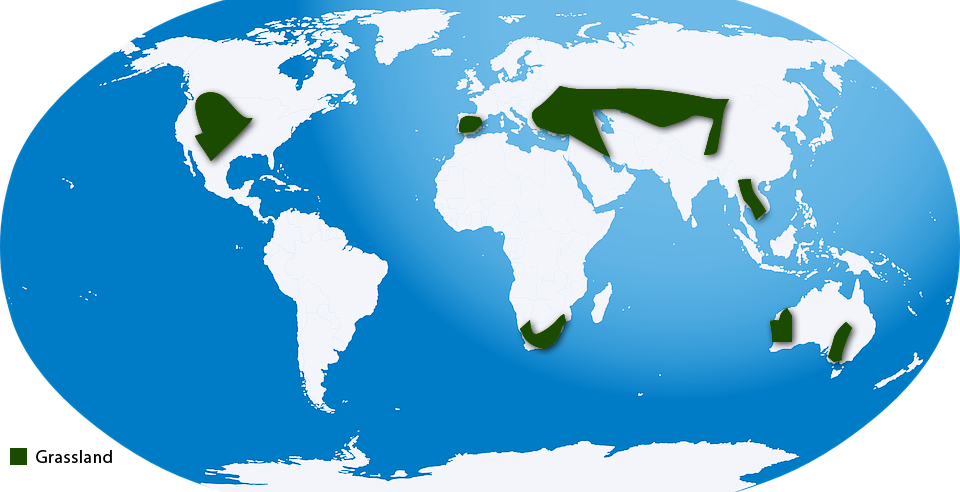
Grasslands are also known as prairies, pampas, steppes, and savannas. ‘Grass’ is the most important plant in this ecosystem. The temperate grasslands have some of the darkest, richest soils.
Grasslands experience hot summers and cold winters. They do not receive enough rain, somewhere between what a forest and a desert receive. Due to less rainfall, one find here lot of grass instead of trees.
Grasses such as purple needle-grass, wild oats, foxtail, ryegrass, and buffalo grass are common in grasslands. Trees and large shrubs are rarely found here. Sunflowers, clovers, wild indigos are few examples of flowers found in this region. Animals such as antelopes, falcons, and fox birds, are common to this ecosystem.
Rainforests can be divided into temperate and tropical rainforests. The tropical rainforests cover around 7% of the Earth’s surface and are home to half of the plant and animal species on Earth. Tropical rainforests are referred to as "jewels of Earth" and the "world's largest pharmacy." About 1/4 of natural medicines have been discovered in rainforests. The soil in the tropical forests is poor in nutrient, as leaching of nutrients takes place due to heavy rainfall.

Temperate rainforests are wet, but not as much as tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests are much more. wet and humid.
Broad-leafed trees such as coffee, brazil nut tree, rubber tree are found in rainforests. Plants such as ferns, vines, mosses, palms and orchids are also found here. Tropical rainforests are home to half the plant and animal species on Earth.
Savannas are characterised by a very dry season and then a very wet season. They are also known as tropical grasslands and are found to the north and south of tropical rainforests. Savannas are found in Africa, South America, India, and Australia. Africa houses the largest expanses of savannas. The soil found here is porous, and witnesses rapid drainage of water.
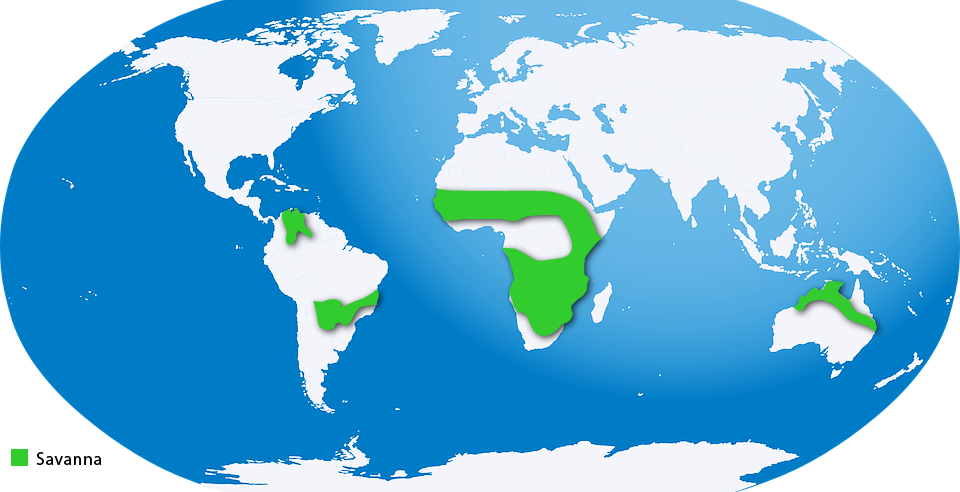
Savannas experience two distinct seasons, a wet season that lasts up to 6-7 months and a dry season of 4-6 months. It receives about 59 inches of rain. The dry season witnesses very little rain.
The plants in Savannas are adapted to the long dry season. Grasses common in Savannas include rhodes grass, red oats grass, star grass, and lemon grass. Trees such as pine trees, palm trees, and acacia trees are commonly found here. Animals such as elephants, zebras, horses, giraffes, rhinos, cheetahs, lions, ostrich, and peacock are common to this ecosystem.
Taiga is the largest terrestrial ecosystem on earth. It experiences short, and wet summers, while long, and cold winters. It is also known as coniferous forest or boreal forest. They are found in Canada, northern Asia, Siberia, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland. About two-thirds of the world's boreal forests are found in Scandinavia (Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland). This ecosystem has thin soil, as decomposition takes a long time due to cold.
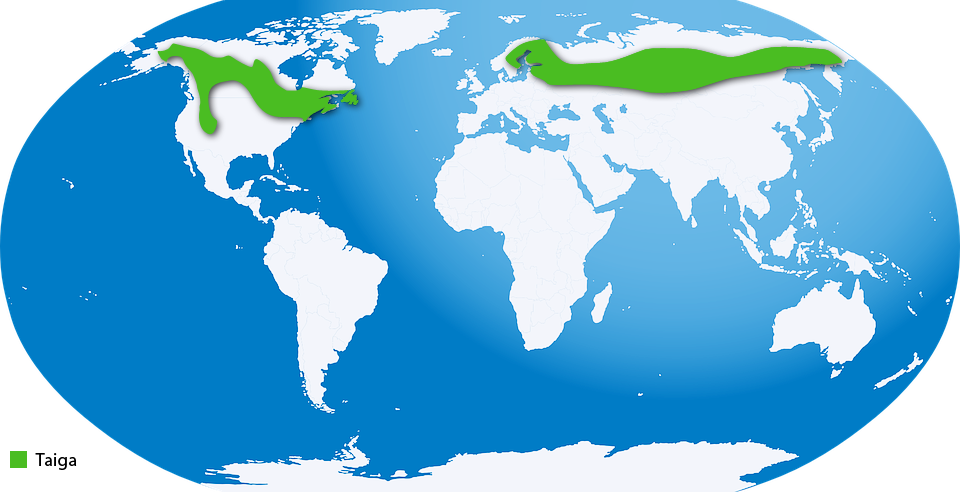
Taiga receives plenty of snow during winters and plenty of rainfall during summers. It receives snowfall between 15 and 40 inches per year.
Due to extreme cold weather, there is less diversity in plants in Taiga. Mostly coniferous trees, also known as evergreens (that do not shed leaves) such as spruce, hemlock, fir and pine are common to this ecosystem. Animals like deer, moose, arctic fox, arctic wolves, snow owls, and snow geese are found in the Taiga.
Tundra is the coldest of all the ecosystems. It covers about one fifth of the land on earth. Vegetation in Tundra is low due to the permafrost soil, which is low in nutrients and remains frozen. Arctic tundra, Alpine tundra and Antarctica tundra are the three types of Tundra region found across the globe. Tundra is located in the Arctic Circle.
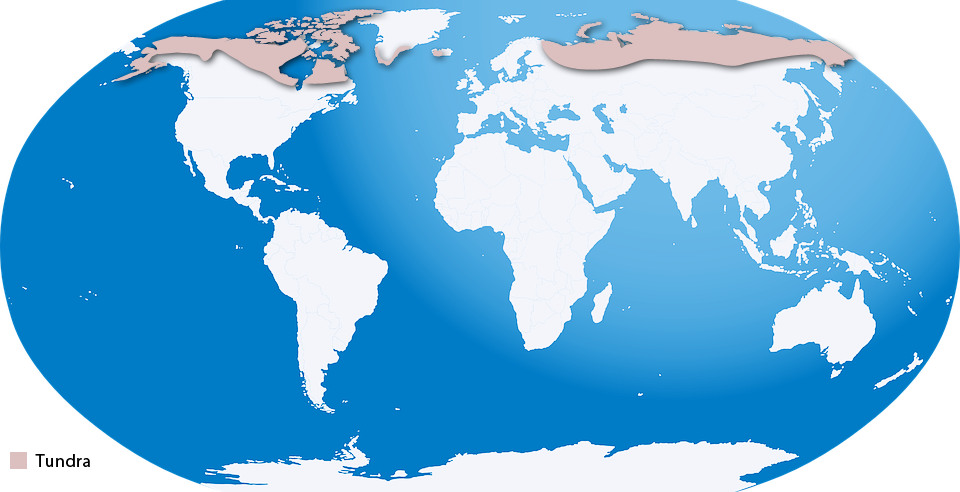
Tundra receives very little rainfall; it rains less than ten inches a year. It experiences long winters, with temperatures dropping below -34° C. The summers are short, which last for only 6 - 10 weeks. and the temperatures are still very cold ranging from 3° to 12° C.
Lichens, mosses, and small shrubs flourish in this ecosystem. Plants such as bearberry, arctic moss, caribou moss, and Diamond leaf willoware commonly found here. Animals common to this ecosystem include the arctic tern, snow geese, tundra swans, and snow owl.


 Biodiversity
Biodiversity